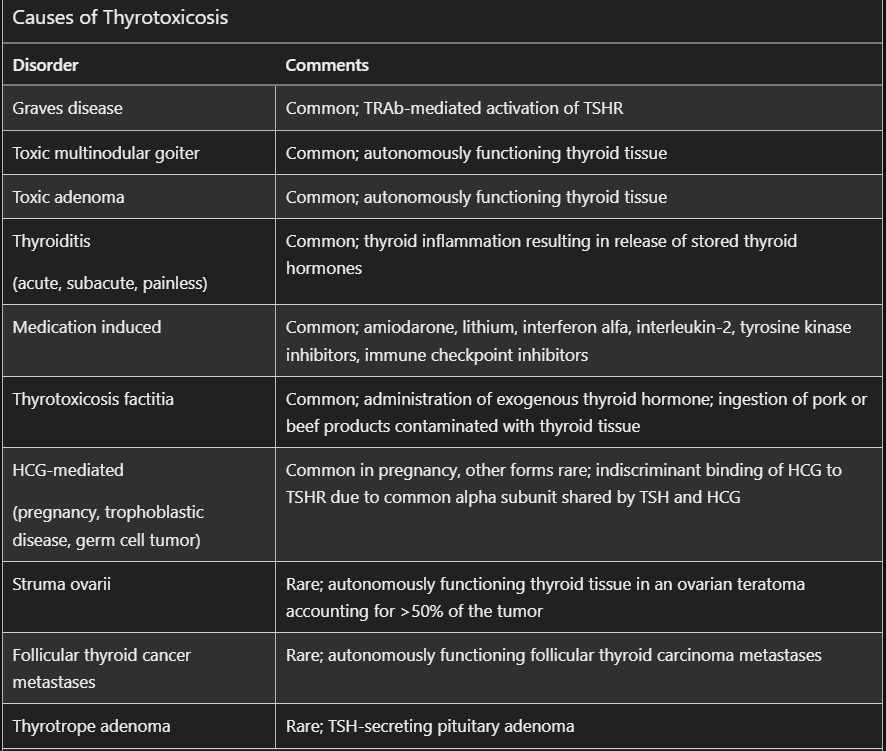
Hyperthyroidism
Presentation :
Pathophysiology :
Diagnostic Testing:
- Serum TSH and free T4
- If TSH is suppressed but T4 is normal, order free T3 to diagnose T3 toxicosis (rare)

- If TSH is suppressed but T4 is normal, order free T3 to diagnose T3 toxicosis (rare)
- Intake of exogenous thyroid hormone suppresses thyroglobulin levels, which makes its measurement useful (when low) in patients with thyrotoxicosis caused by surreptitious use of thyroid hormone
- Antibodies need not be checked routinely in the evaluation of hyperthyroidism unless the diagnosis is unclear
- TSH-receptor antibodies and thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins are associated with Graves disease
- An elevated serum ESR supports thyroiditis
Treatment :
- Propranolol to rapidly reduce adrenergic symptoms
- Propranolol in particular among BBs inhibits the peripheral conversion of T4 to the more biologically active hormone, T3 via inhibition of 5'-monodeiodinase
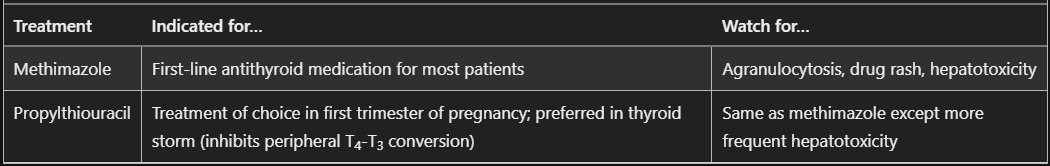
- In pregnancy, PTU is used for 1st trimester, Methimazole in 2nd + 3rd
Radioactive iodine is used for toxic multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, and Graves disease (usually following failed drug therapy) - Contraindicated in pregnancy or breastfeeding
- May aggravate Graves ophthalmopathy unless pretreated with glucocorticoids
- In pregnancy, PTU is used for 1st trimester, Methimazole in 2nd + 3rd
- Thyroidectomy is preferred as definitive therapy for hyperthyroidism in large goiter with compressive symptoms, or in pts
intolerant of other therapies - Treatment of subclinical hyperthyroidism is recommended for patients with thyroid-stimulating hormone level less than 0.1 μU/mL (0.1 mU/L) and cardiac risk factors, heart disease, high risk for osteoporosis, or symptoms.
Prognosis:
References:
- MKSAP
- https://www.ebmconsult.com/articles/propranolol-preferred-thyroid-storm-thyrotoxicosis
- The influence of beta-adrenoceptor blocking agents on plasma thyroxine and triiodothyronine
Created on: Friday 08-11-2023