Hypocalcemia
Presentation :
- Mild: perioral numbness, paresthesias of the hands and feet, muscle cramps (Chvostek + Trousseau sign; see below)
- Severe: carpopedal spasm, laryngospasm, and focal or generalized seizures
Pathophysiology :
- Etiologies include
- Hypoparathyroidism
- Vitamin D Deficiency
- Chronic Kidney Disease
- hungry bone syndrome
- Osteoblastic metastases (prostate cancer, breast cancer)
- Antiresorptive drugs, such as intravenous bisphosphonates and denosumab
- Therefore, it is important to assess vitamin D levels and correct deficiency before beginning treatment with an antiresorptive drug.
Diagnostic Testing:
- EKG to assess for QTc prolongation
- If low albumin or concurrent acid/base disorder, consider verifying with ionized Ca measurement
- Check Mg level
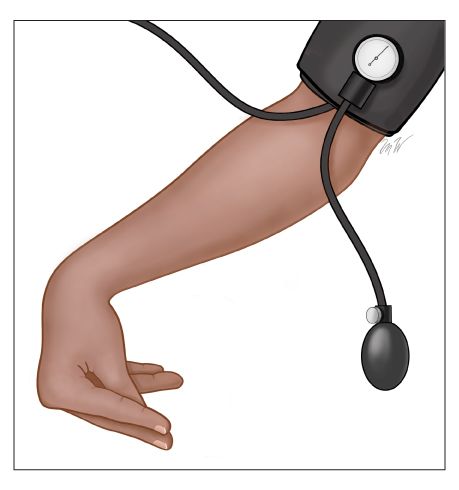
- Trousseau's sign: induction of carpal spasm by inflation of a sphygmomanometer above systolic blood pressure for three minutes
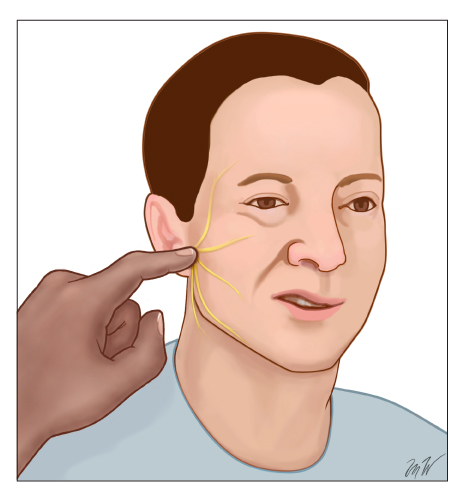
- Chvostek's sign: contraction of the ipsilateral facial muscles elicited by tapping the facial nerve just anterior to the ear
Treatment :
- Severe hypocalcemia (<7.5 mg/dL; prolonged QT interval; symptoms)
- Telemetry
- IV calcium gluconate
- Mild hypocalcemia:
- Vitamin D supplementation, 1000-4000 IU/day AND Calcium carbonate/citrate PO 1-3 g/day in divided doses taken with meals
- Must correct coexisting hypomagnesemia!
- Teriparatide, 20 μg twice daily, rapidly eliminates symptoms of hypocalcemia in acute postsurgical hypoparathyroidism
Prognosis:
References:
Created on: Friday 08-11-2023