Pyoderma Gangrenosum
Presentation :
- Rare
- Most commonly presents w/ inflammatory papule or pustule that progresses to a painful ulcer with a violaceous undermined border and a purulent base.
- Lesion development is often rapid and the level of pain is often greater than expected based upon the appearance of the ulcer
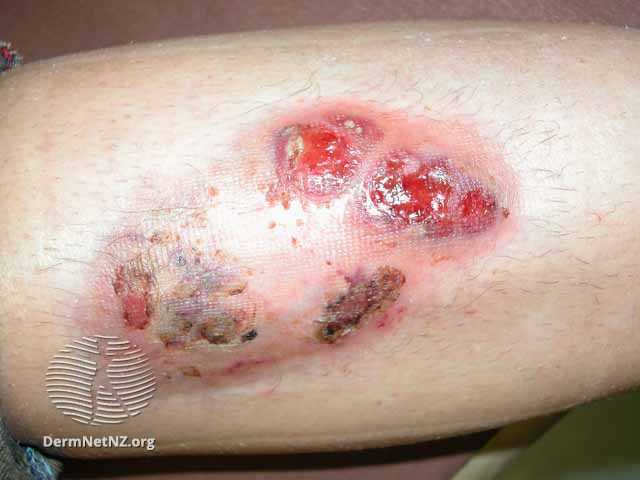
- Often associated with an underlying autoimmune disease (IBD, RA, Ankylosing Spondylitis), heme malignancies, and heme diseases (MGUS, MDS, Polycythemia vera), post-surgical
Pathophysiology :
- Inflammatory neutrophilic dermatosis
Diagnostic Testing:
- Diagnosis of exclusion
- Biopsy is required, will require derm consultation
- Optimal is an elliptical incisional biopsy w/ inflamed lesion border + ulcer edge extending vertically into SubQ fat
- 1 major and 4 minor criteria for diagnosis:
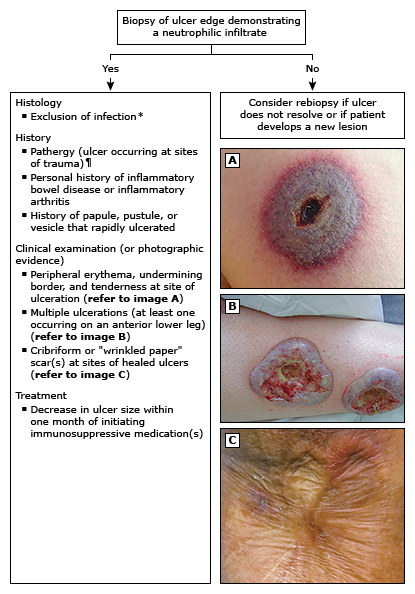
Treatment :
- Limited disease = single or few small (<3 cm), superficial ulcers:
- High potency corticosteroid cream
- If insufficient can switch to topical tacro OR add oral minocycline/dapsone
- Proceed to treatment for extensive disease
- Extensive disease:
- Start w/ Oral Prednisone
- Oral cyclosporine if prednisone is contraindicated
- Add infliximab, adalimumab, or mycophenolate mofetil if treatment failure; some derm will use this at time of oral therapy initiation for a few weeks as well
Prognosis:
-
50% achieve wound healing within one year, and almost all patients achieve remission with more prolonged treatment.
- Relapses can occur after long periods of disease remission
References:
- https://dermnetnz.org/topics/pyoderma-gangrenosum
- https://www.uptodate.com/contents/pyoderma-gangrenosum-pathogenesis-clinical-features-and-diagnosis
- https://www.uptodate.com/contents/pyoderma-gangrenosum-treatment-and-prognosis
Created on: Saturday 06-08-2024